Optical fiber network optimization guide: fiber patching and fiber placement principles
Optical fiber network optimization guide: fiber patching and fiber placement principles
This guide explores critical techniques for working with fiber patch cords (jumpers) and deployment best practices. We’ll cover handling, labeling, bend-radius compliance, polarity, routing infrastructure, disaster recovery, and emerging trends—creating a strong foundation for fiber‑based network excellence.
Introduction
Modern optical networks underpin everything from data centers and telecom backbones to campus infrastructures and fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) environments. However, merely deploying fiber isn’t enough—optimal patch-cord management and routing practices are essential to realize peak performance, longevity, and reliability.
This guide explores critical techniques for working with fiber patch cords (jumpers) and deployment best practices. We’ll cover handling, labeling, bend-radius compliance, polarity, routing infrastructure, disaster recovery, and emerging trends—creating a strong foundation for fiber‑based network excellence.
Part 1: Handling Patch-Cords With Care
1. Cleanliness Is Key
Contaminants on connectors cause insertion loss, reflection, or even physical damage.
Always inspect ferrules before mating using an inspection probe.
Clean with lint-free wipes and 99% isopropyl alcohol before connections.
Keep dust caps on until the final connection step.
Store spare patch cords in clean bags with humidity control.
2. Maintain Bend Radius and Tensile Limits
Fiber’s glass is fragile—protect it at every turn.
Adhere to each cable’s specified minimum bend radius (typically 10× the cable diameter).
Use slack loops and avoid sharp bends—especially near termination points.
Enforce tensile limits—no pulling on fibers for alignment or routing.
Utilize slack management panels instead of free-hanging cable excess.
3. Use Structured Routing Infrastructure
Structured pathways ensure fiber integrity and traceability:
Use cable trays or ladder racks above equipment for horizontal management.
For vertical runs, use cable risers or floor ductwork that are secure and accessible.
In racks, route fibers in tray systems with integrated strain relief.
Label racks, patch panels, and cables consistently with permanency (e.g., engraved tags).
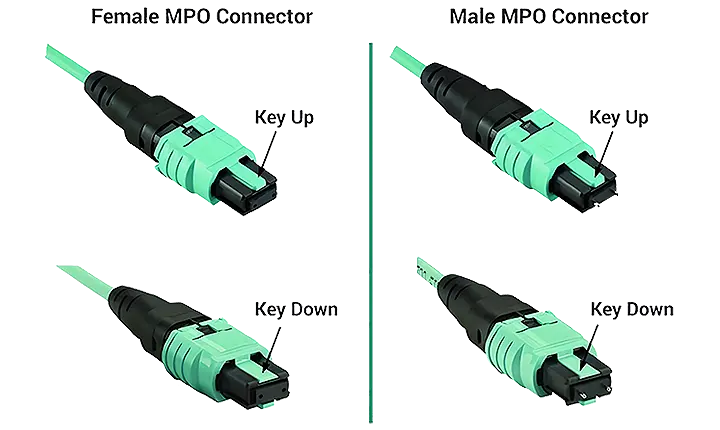
4. Maintain Polarity and Connection Order
Correct polarity ensures transmitter‑to‑receiver routing.
Duplex LC cables need consistent direction (A to B fiber pair).
MPO trunk cables require correct polarity (Method A/B).
Label each patch cord with its orientation and sequence number.
Use color-coded boot designs to indicate polarity or function.
5. Avoid Midspan Connector Use
Midspan connectors complicate cabling and raise failure potential:
Prefer continuous cable lengths between endpoints.
If a cable must be extended, use a patch panel to maintain visibility and testing control.
Part 2: Fiber Routing & Deployment Best Practices
1. Follow Structured Cabling Standards
Standards (e.g., TIA/EIA, ISO/IEC) offer formal guidelines:
Maintain consistent outlet locations and equipment topology.
Respect maximum cable lengths (e.g., 90 m for 10G OM3 multimode).
Organize cable numbering and charting for documentation.
2. Preserve Proper Bend Radius Continuously
Cables bend every time they route corners:
Use pre-installed cable guides in cabinets and under raised floors.
Install bend radius limiters on racks and ducts.
For flexible patch cords, use articulated cable arms on closer terminations.
3. Implement Slack Management Tactics
Slack loops are necessary but must be controlled:
Pre-make figure‑8 loops for extra length.
Use cable lacing bars to secure excess neatly.
Label slack loops for future reference or maintenance.
4. Practice Cable Segregation
Signal integrity benefits when fiber is isolated:
Avoid co‑routing with power cables to prevent EMI/RFI risks.
Lay cable trays for fiber above power trays.
Keep fiber in a separate conduit when sharing ducts with electrical wiring.
5. Optimize Workspace and Labeling
A clear workspace prevents tangles and errors:
Assign each cable a unique identifier (rack‑unit, panel‑port, destination).
Keep label rims close to termination ends for clarity.
Update documentation notes whenever changes occur.
6. Create Accessible Routing Topology
Physical access improves troubleshooting:
Position fibers on the front side of racks when possible.
Use sliding patch trays for 1U or 2U cabinets.
Maintain proactive cable grooming schedules (quarterly reviews).
Part 3: Managing Patch-Cord Infrastructure
1. Build a Labeled Patch Panel Ecosystem
Patch panels serve as management hubs:
Use modular cassettes for high‑density MPO to LC conversion.
Keep front panels scannable and connectors visible.
Record each port’s mapping (e.g., floor→rack→switch port).
2. Choose Correct Patch-Cord Lengths
Avoid slack excess or strain:
Measure runs precisely for minimal slack allowance.
Use standard small lengths for horizontal connections (e.g., 1–3 m).
Use longer 5–7 m cords to connect patch panels to cross‑connect blocks.
3. Inventory & Stock Management
Spare cables save downtime—stock wisely:
Maintain color-coded inventory.
Store new cords sealed with humidity/spoiler protection.
Perform yearly audits to match stock against installed inventory.
4. Clean and Inspect Actively
Fiber performance degrades over time through contact cycles:
Establish quarterly connector inspection routines.
Clean connectors after any un-mating event.
Use pass/fail tools to monitor link loss thresholds.
Part 4: Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Diagnosing High Loss
Loss above expected levels? Check for:
Dirty, scratched, or broken connectors.
Cable bends violating radius specs.
Mid-span connectors or unplanned splices.
Use an optical power meter or OTDR to localize faults.
2. Eliminating Reflectance & Crosstalk
High reflectance can impair high-speed signals:
Ensure proper UPC/APC polish matches.
Ensure connector types or keying haven’t been mixed.
For 400G+, preserve end-surface quality better than 50 ms.
3. Re-polishing or Replacing Damaged Cables
Damaged connectors or cables must be replaced:
Only qualified technicians should re-terminate.
Document every replacement and remark in diagrams/lustres.
4. Fixing Polarity Mix-Ups
Detect mid-connection misalignments:
Verify transmitter directly drives the intended receiver.
Perform loopback testing.
Label misaligned LO inputs/outputs and rearrange connectors.
Part 5: Guidelines for MPO & High‑Density Deployments
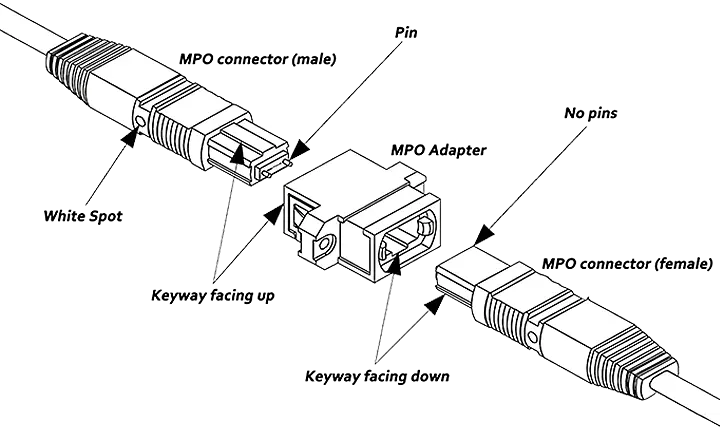
1. Complex MPO Polarity Management
MPO systems add density but require care:
Use Type A/B polarity reference standards.
Label each trunk, cassette, and patch for clear mapping.
Overlay on logical diagrams tied to physical patch layouts.
2. Preserving Bend Radius on MPO Trunks
With thicker ribbon cables:
Use trough retentive trays and flat trays.
Avoid uncontrolled slack—figure‑8 loops control stacking.
Keep tray clean and dust‑free.
3. Clean Connectors Between Patch-to-Patch
Don’t forget inter-panel connections:
Clean MPO connectors at every mating cycle.
Use dedicated MPO cleaning reels or cassettes.
4. Prepare for Capacity Growth
With 40/100/400/800G solutions:
Leave cable trays with spare space (30–40% headroom).
Leave ports empty for future expansion.
Use modular panels and LC cassettes for easy upgrades.
Part 6: Documentation & Traceability
1. Create Hierarchical Labeling Schemes
Label from floor → rack → panel → port and record each:
E.g., “B2R3–PWR–F01–S12 → SW1:1/13” works well.
2. Keep Accurate Cabling Maps
Use CAD, Visio, or IPAMS tools to map connectivity:
Plan fiber routes in software.
Add notes for special ports (e.g., SR, AOC, breakout).
3. Log Changes Rigorously
Every physical change needs updating:
Use clear change control steps.
Archival diagrams reflect past configurations.
4. Employ Test Reports
Each deployment should include test sheet:
Include loss graphs and pass/fail data.
Store electronically for compliance.
Part 7: Safety, Standards & Best Practices
1. Know Fiber Safety
Invisible light harms eyes:
Never stare into connector ends.
Use laser‑safe procedures.
Wear gloves to prevent contamination.
2. Follow Regulatory Standards
Maintain compliance with:
ISO/IEC 11801, TIA‑942, BICSI, IEEE 802.3, etc.
Observe fire and plenum codes (CMP vs. PVC jackets).
Ground cabinets per building codes and NFPA standards.
3. Adopt Green Deployment
Use OM4 or OM5 multimode for longer-reach yet ambient savings.
Use breakout modular cassettes to reduce patch-cord bulk.
Replace sporadic patching with trunk-and-cassette setups.
Conclusion
A well-optimized fiber network requires disciplined handling, routing, labeling, cleaning, documentation, and planning. Following these patch‑cord and routing principles ensures your network delivers:
Longevity and minimal degradation
Predictable high performance
Simplified upgrades
Reliable maintenance and quick problem isolation
By investing in best practices today, your fiber infrastructure becomes more resilient, streamlined, and ready for tomorrow’s ever‑growing bandwidth demands.









 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.