MPO Technology – A Cost-Effective 40G Ethernet Solution
MPO Technology - A Cost-Effective 40G Ethernet Solution
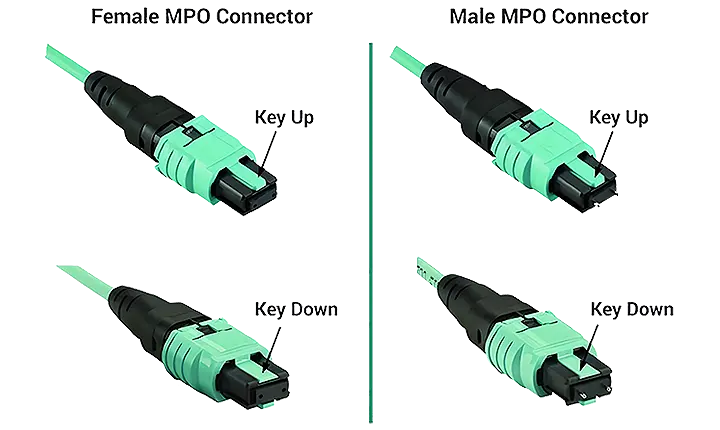
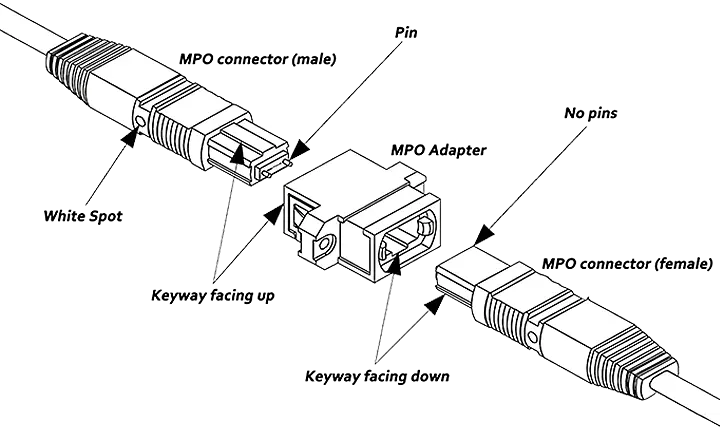
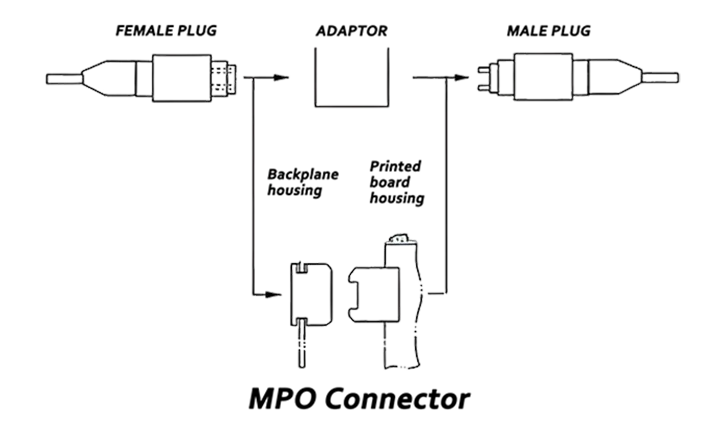
MPO connectors are available in two styles: male and female. The male version includes alignment pins, which ensure accurate core positioning and prevent signal misalignment. Female connectors lack these pins and are used in conjunction with male connectors to form proper mated pairs.
Empowering High-Speed Networks with MPO Technology: Practical Applications and 40G Ethernet Deployment
As demand for high-performance data transmission continues to rise, MPO (Multi-fiber Push On) technology plays a critical role in building scalable and efficient data center infrastructures. With its innovative multi-fiber interface, MPO simplifies the transition to 40G and 100G Ethernet, while offering exceptional scalability for future network expansions. This article explores the real-world application of MPO components and its role in modern structured cabling systems.
Understanding MPO Assemblies
To begin, let’s examine the structure of an MPO connector. MPO supports up to 72 fiber cores within a single interface, enabling dense interconnections. Ensuring precise alignment and connector stability at both ends is essential to achieving reliable optical performance. Improper connections can lead to insertion loss, network failure, or even damage to the connector itself.
MPO connectors are available in two styles: male and female. The male version includes alignment pins, which ensure accurate core positioning and prevent signal misalignment. Female connectors lack these pins and are used in conjunction with male connectors to form proper mated pairs.
Alignment and Adapter Design
MPO connectors are keyed for proper orientation. They include a guide pin (key) and groove on the housing to ensure correct mating. There are two adapter configurations:
Key-Up to Key-Down (Type A) – One connector’s key faces upward while the other’s key faces downward. This setup allows a 180° rotation for polarity matching.
Key-Up to Key-Up (Type B) – Both keys face upward, keeping the connectors in the same orientation.
Note: APC-polished (Angled Physical Contact) MPO connectors, which feature an 8° angled end face, are typically used in single-mode applications and require Type A adapters for proper interfacing.
Key Connection Guidelines
To form a proper MPO link, follow these core rules:
Always use one male and one female connector, along with an MPO adapter. This ensures proper alignment and maintains transmission quality.
Never mate two male connectors or two female connectors. Two female connectors will result in poor core alignment due to the absence of guiding pins, leading to signal loss. Two male connectors, on the other hand, will have pin collision, possibly damaging the connectors.
Do not disassemble MPO connectors. The alignment pins are not designed for removal, and attempting to do so may damage the internal fibers. Tampering with the housing may also void any warranty.
MPO Patch Cord Varieties
MPO patch cables are prized for their installation speed, consistency, and reliability. Here are the key types commonly used in high-speed network environments:
MPO Trunk Cables
MPO trunk cables are ideal for connecting to MPO modules or panels, forming a permanent link within the infrastructure. Available in 12, 24, 48, and 72-core configurations, these cables are pre-terminated to ensure optimal performance.
The connector types and pin assignments can be tailored according to user requirements. By using MPO trunk cables, businesses can implement cost-effective, structured 40G cabling systems with reduced deployment times and lower installation costs. Pre-planning is essential, but once installed, the benefits include consistent quality, easier cable management, faster setup, and future-proofing.
MPO Breakout Cables
MPO breakout or fan-out cables offer conversion between multi-core MPO connectors and multiple single-fiber interfaces. For example, an 8-fiber MPO breakout cable can connect to eight LC connectors, allowing for straightforward integration into 40G applications while maintaining clear, organized routing.
Y-Cables for Migration
Y-shaped cables enable 2-to-1 or 3-to-1 aggregation. A typical application involves combining two 12-core MPO trunk cables into a single 24-core cable, a strategy useful in transitioning to 100G environments. Another variation might involve three 8-core MPO connectors linking to a single 24-core trunk, supporting permanent 40G connections with enhanced flexibility.
Deploying MPO for 40G Ethernet
Parallel optical transmission, used in 40G networks, requires OM3 or OM4 multimode fibers arranged in MPO patch cables. The small diameter of these fibers ensures ease of installation, even in constrained spaces.
However, high-speed ports designed for parallel transmission demand significantly more fiber cores per connection—making traditional simplex or duplex connectors insufficient. The MPO interface solves this limitation by accommodating multiple fibers through a single port, thus enabling parallel communication without signal degradation.
This approach simplifies port expansion and high-density interconnects, particularly in core-switching or Top-of-Rack (ToR) architectures.
Real-World Application of MPO in 40G Networks
MPO connectors and patch cords are the essential building blocks for establishing functional 40G optical links. Several factors determine the success of a 40G deployment:
Insertion loss must remain below the link’s attenuation budget.
Return loss must meet defined thresholds to prevent back-reflection.
The total bandwidth of the channel must align with application demands.
MPO-based cabling systems make it possible to maintain these parameters consistently, helping ensure that 40G deployments meet both immediate and future performance requirements.
Summary
In conclusion, MPO technology has proven to be a reliable foundation for high-speed data center networks. Its ability to support parallel optical links simplifies the migration path to 40G and 100G, enabling faster, cleaner, and more efficient deployments.
MPO connectors and patch cables offer a compact, scalable, and standardized solution for managing high-density fiber links. As optical networks evolve to support growing traffic and AI-driven workloads, MPO infrastructure will remain central to ensuring that data centers can keep pace with next-generation demands.
By following correct installation practices and understanding the different MPO component types, organizations can leverage this technology to build networks that are agile, future-ready, and operationally efficient.









 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.