Data Center Cabling Solution—MTP & MPO Cabling System
Data Center Cabling Solution—MTP & MPO Cabling System
MTP solutions are not only essential for meeting modern bandwidth
demands but also for building future-proof, space-saving, and cost-effective data center networks.
With the growing demand for higher bandwidth in data centers, high-speed transmission has become a key trend in cabling infrastructure. Utilizing MTP/MPO components for structured MTP/MPO cabling (hereafter referred to as MTP) has become a widely accepted and efficient solution for building high-performance networks in today’s data centers.
This article will explore the importance and necessity of high-density MTP cabling systems, and provide an overview of the various MTP components involved.
Background of MTP Cabling
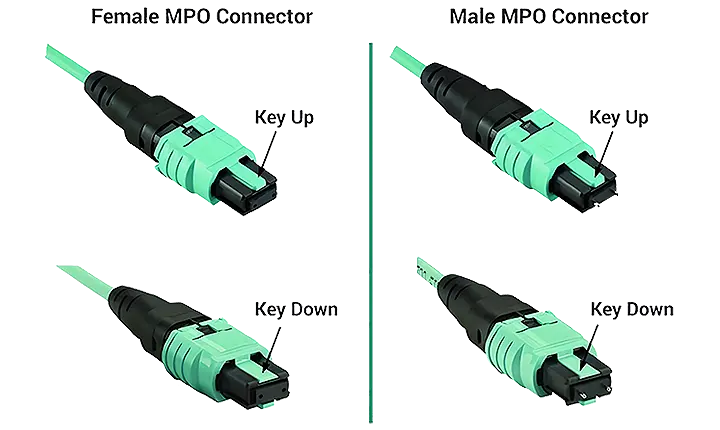
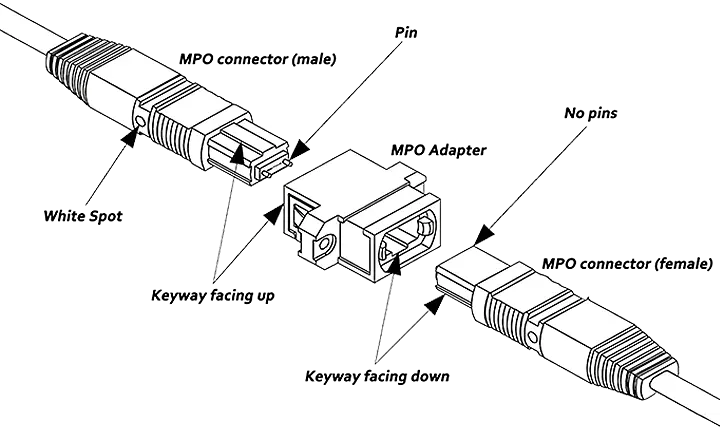
Traditionally, tight-buffered multi-fiber cables require skilled technicians to manually terminate both ends. In contrast, advanced MTP patch cords come pre-terminated, with MTP connectors on each end capable of housing multiple fibers. The most common configurations are 12-fiber and 24-fiber, with support for up to 72 fibers. MTP connectors are available in male (with pins) and female (without pins) versions. The development of MTP technology meets the needs of large-capacity fiber systems, making it an optimal solution for achieving high-density and high-performance connectivity in data centers.
MTP Cabling Solutions – A Modern Trend in Data Center Infrastructure
Traditional LC cabling systems are no longer sufficient to handle the increasing demands for high-speed transmission and port density in large-scale data centers. As a result, many IT professionals are now turning to MTP-based cabling solutions. Unlike conventional LC systems, MTP cabling offers superior support for high-speed, high-density, and structured cabling needs. Key benefits of MTP solutions include:
1. Robust and Reliable
The unique ferrule design of MTP connectors enhances signal stability and significantly improves durability, reducing the chances of signal disruption over time.
2. High Density and Scalability
MTP connectors are compliant with Telcordia (formerly Bellcore) standards and have been used across various telecom environments for over a decade. They solve the challenge of fitting many fibers into limited space. For instance, a 1U chassis using LC duplex connectors can accommodate 144 fibers, whereas an MTP setup can support up to 864 fibers—nearly six times more.
3. Time-Saving and Efficient Deployment
Manually terminating and testing 144 fibers could take a full day for a technician. However, using pre-terminated MTP cables with 12 or 24 fibers and integrated latching tools significantly shortens installation time. Plug-and-play solutions reduce deployment effort even further and result in lower maintenance costs.
4. Future-Ready Network Scalability
MTP cabling supports direct connections for 40G, 100G, 200G, and even 400G systems. It is widely adopted for upgrading 10G networks to higher bandwidths like 40G, 100G, or 120G, offering a cost-effective and scalable path forward. It also supports uplinks between devices operating at different speeds—such as 25G to 100G, 50G to 200G/400G, or 100G to 400G.
5. Structured Cabling for Rack Systems
Structured MTP cabling creates a layered architecture in the network, with aggregation points simplifying connectivity and reducing cable clutter. When future expansion is needed, an MTP structured cabling system offers a flexible and scalable solution that supports long-term infrastructure goals.
MTP patch cord products: diverse needs, multiple choices
MTP cabling series products are diverse and can meet different application needs, including MTP patch cords, MTP distribution boxes, and MTP-LC branch cables.
MTP Trunk Cables:An MTP trunk cable consists of a single fiber optic cable terminated with MTP connectors on both ends. It serves as a key component for linking optical transceivers, forming a complete transmission path. These cables are available in configurations supporting 8, 12, 16, 24, 32, 48, or even up to 72 fibers, making them ideal for meeting the requirements of high-density cabling environments.
There are two primary application scenarios:First, MTP trunk cables can be used for direct connections between optical modules, such as 40GBASE-SR4/PLR4, 100GBASE-SR4/SR10, 200GBASE-SR8, and 400GBASE-SR8.
Second, they are commonly utilized in structured cabling setups, connecting patch panels or enclosures. This approach simplifies backbone deployment in dense data center environments and ensures faster, more organized network installation.
MTP Breakout Cables:An MTP breakout cable features an MTP connector on one end that branches out into multiple individual connectors—typically 4, 6, 8, or 12—such as LC, SC, or ST types. These connectors convert a multi-fiber interface into simplex or duplex connections, enabling flexible interconnects within various systems.Breakout cables are available in both single-mode and multimode versions, supporting transmission over short to extended distances. They are an excellent solution for bandwidth upgrades or transitions, such as from 10G to 40G, 25G to 100G, or 10G to 120G networks, providing reliable performance and simplified connectivity.
MTP Conversion Cables:MTP conversion cables, like breakout cables, utilize a fan-out design but feature MTP connectors on both ends. The fiber count and connector types on each side can differ, allowing for a variety of configurations in 24-fiber cabling systems. These cables enable flexible conversions such as 24-fiber to 2×12-fiber, 24-fiber to 3×8-fiber, or 3×8-fiber to 2×12-fiber setups, making them a versatile choice for adapting different MTP link standards within high-density environments.
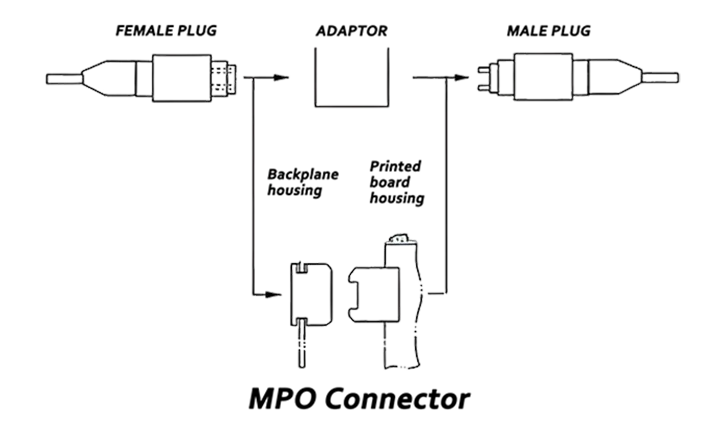
MTP Adapters and MTP Adapter Panels:MTP adapters serve as essential accessories for MTP fiber patch cords. They come in two alignment key configurations: key up-to-key up and key up-to-key down. Both types are designed to connect MTP patch cables to each other or to devices, making them commonly used in backbone cabling and patch panel installations. MTP adapter panels are enhanced assemblies that accommodate multiple adapters within a single frame. Equipped with a secure mounting plate, these panels are a more advanced solution. Pre-installed with adapters, the panels act as an interface between trunk cables and patch cords, offering a compact and dependable network interconnection point for high-density environments.
MTP Fiber Enclosure:The MTP fiber enclosure is a closed box-style unit that typically houses 12 or 24 optical fibers. The front panel features LC or other connector types, while the rear is equipped with an MTP interface. It functions by splitting high-fiber-count trunk cables into multiple duplex connections. When mounted within a rack, the MTP enclosure enables the fast deployment of high-density data center infrastructure. It also allows for easier maintenance, troubleshooting, and reconfiguration of the fiber network during operation.
Rack-Mount MTP-LC Adapter Panel:The 96-fiber pre-terminated MTP-LC rack-mount adapter panel is designed to fit standard 19-inch racks, allowing all 96 fibers to be deployed within a 1U space without the need for additional hardware. When implementing 10G to 40G or 25G to 100G links, MTP trunk cables can be used to connect 40G/100G switch ports to the rear of the panel, while duplex LC patch cords are used to connect 10G/25G devices to the front-facing ports. This type of MTP-LC panel features a removable rear cable management bracket, offering flexible organization of trunk cables. This not only simplifies the installation process but also improves cabling layout and overall system efficiency.
Summary
Clearly, with the widespread adoption of 40G, 100G, 200G, and 400G networks in data centers, the demand for higher speeds and greater density has become undeniable. Traditional LC cabling can no longer meet these rigorous requirements. In contrast, MTP cabling solutions align perfectly with this trend, offering significant advantages in saving time, space, and cost, along with excellent reliability and high-density capabilities. These features make MTP cabling and its components the ideal choice for building high-performance data center networks. Without question, MTP solutions represent the best option for seamless data interconnection and rapid network upgrades.









 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.