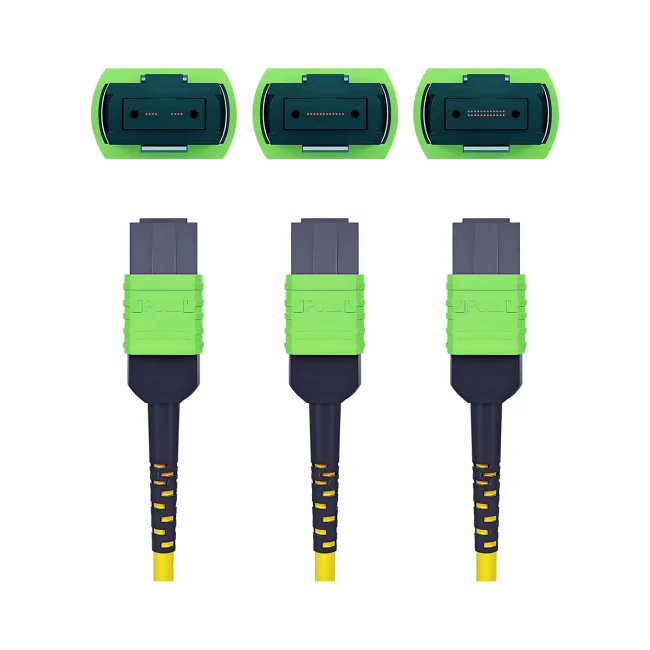
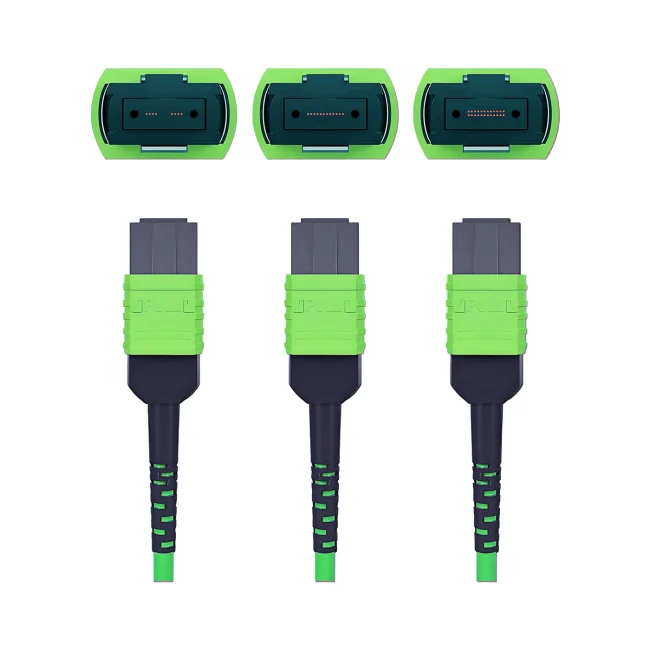
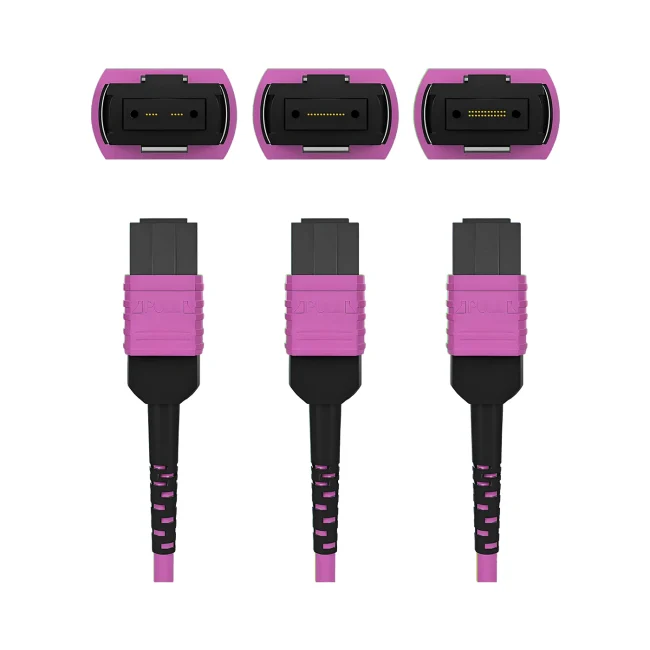
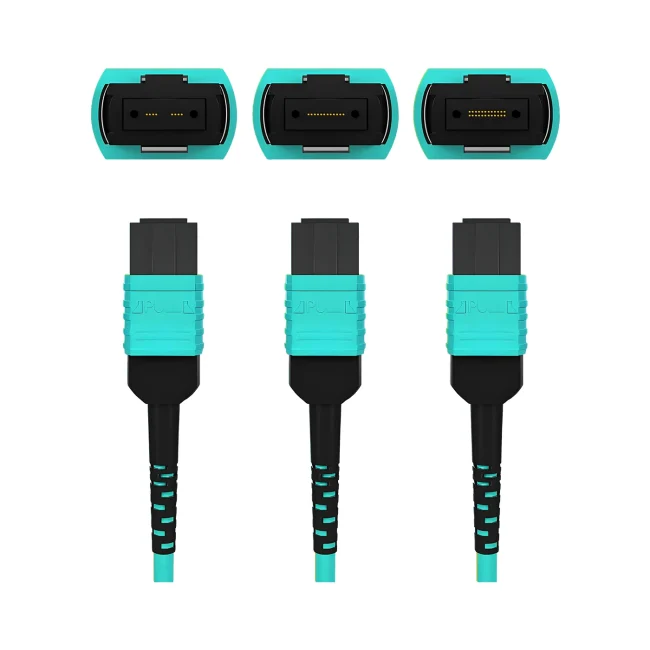
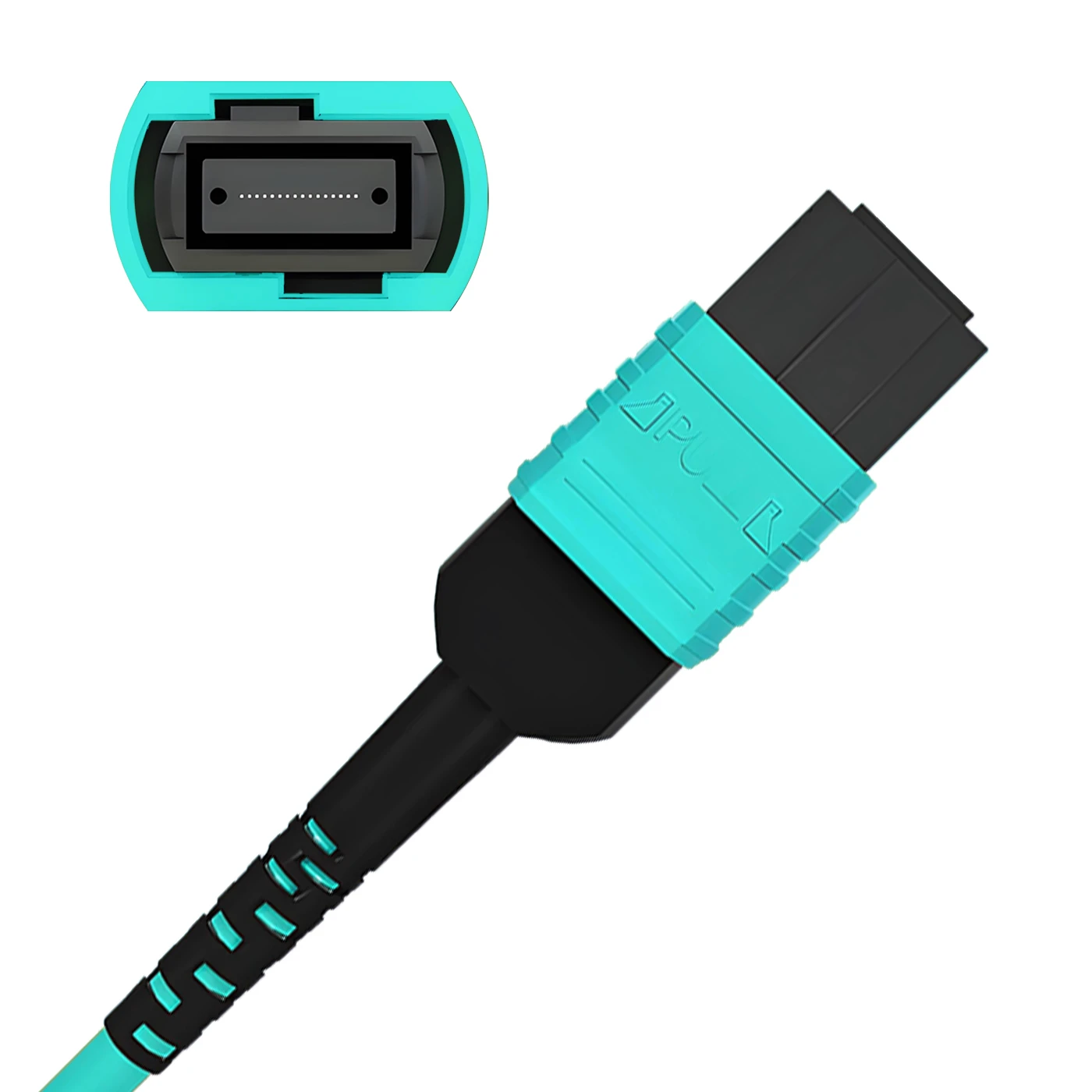
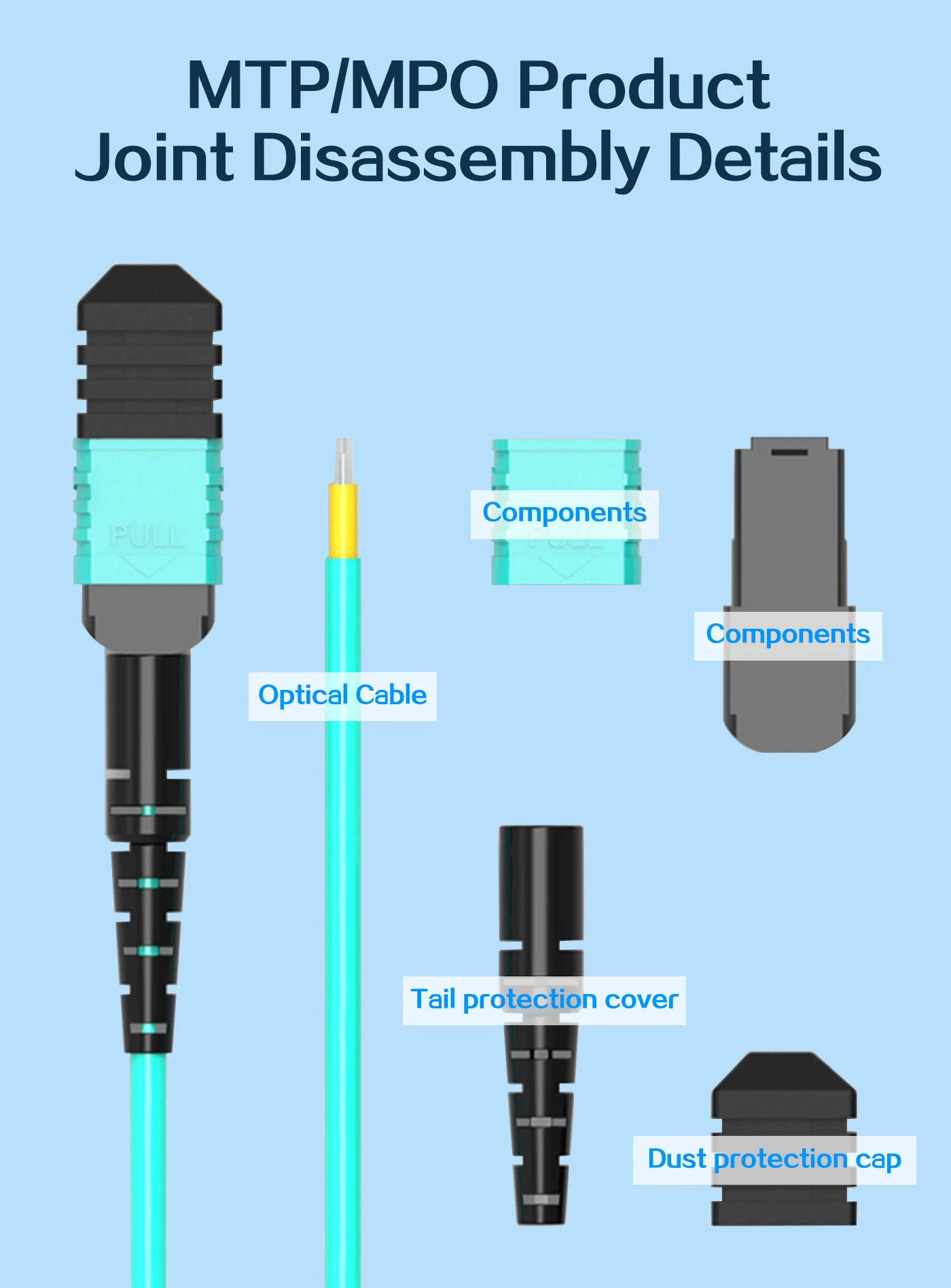
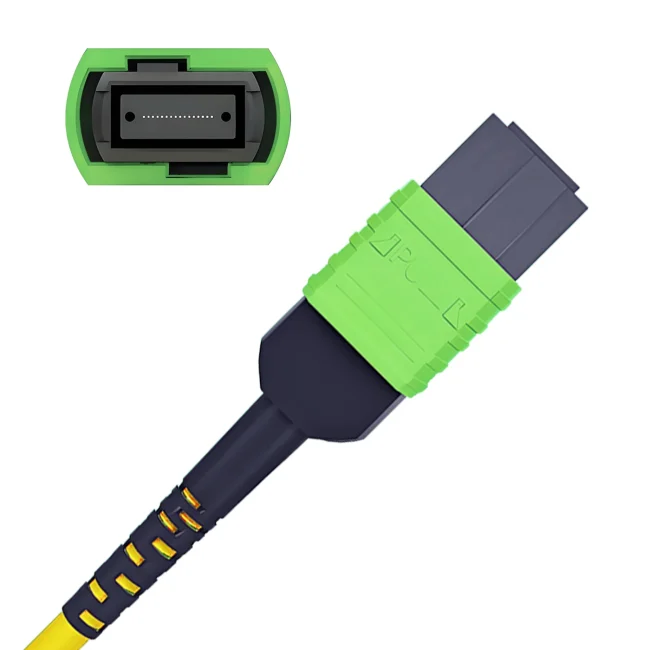
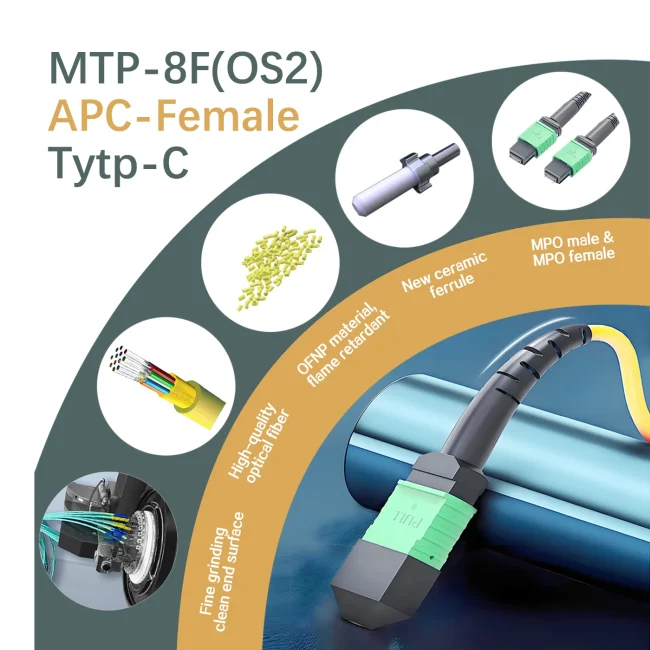
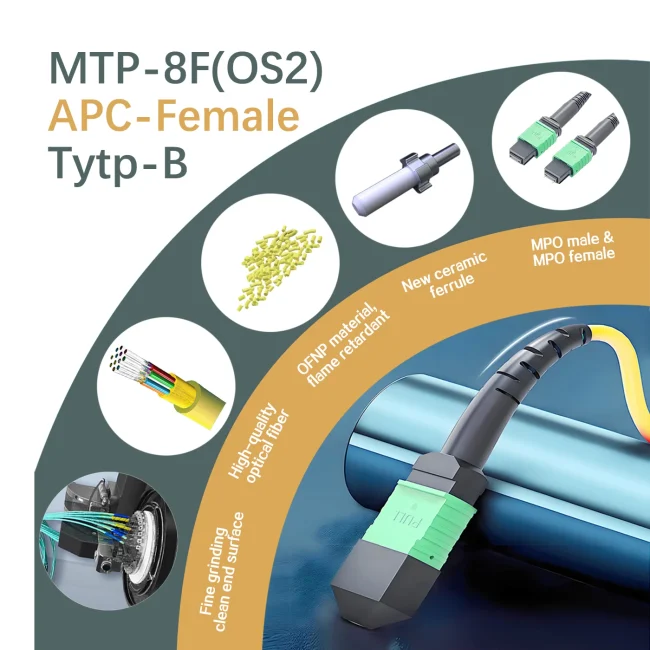
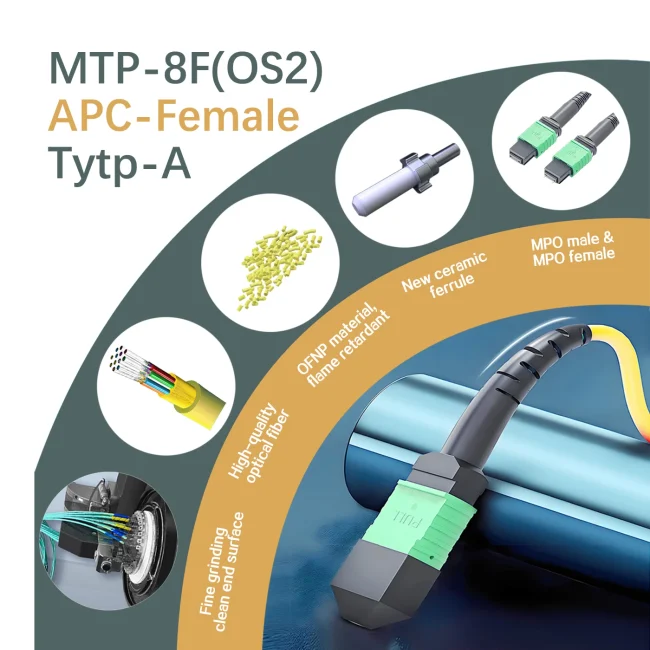
MTP Fiber Patch Cable
MTP® jumpers enable seamless migration to higher data rates in data centers when used together with our trunk cables. They are typically applied for patching within equipment cabinets. MTP® cable, a cost-effective alternative to time-consuming field termination, is specifically designed for high-density fiber patching in data centers requiring space efficiency and simplified cable management.
As MTP®-12 connectors are also compatible with MTP®-8 fiber systems, they are well-suited for 8-fiber parallel multimode optical transceiver applications, including 40G QSFP+ SR4/CSR4 and 100G QSFP28 SR4 optics connections.
Please note: The US Conec MTP® connectors are fully compliant with MPO standards and offer patented innovative features, increased precision, verified durability, and significantly improved performance compared to conventional MPO connectors.
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Advantage Specifications
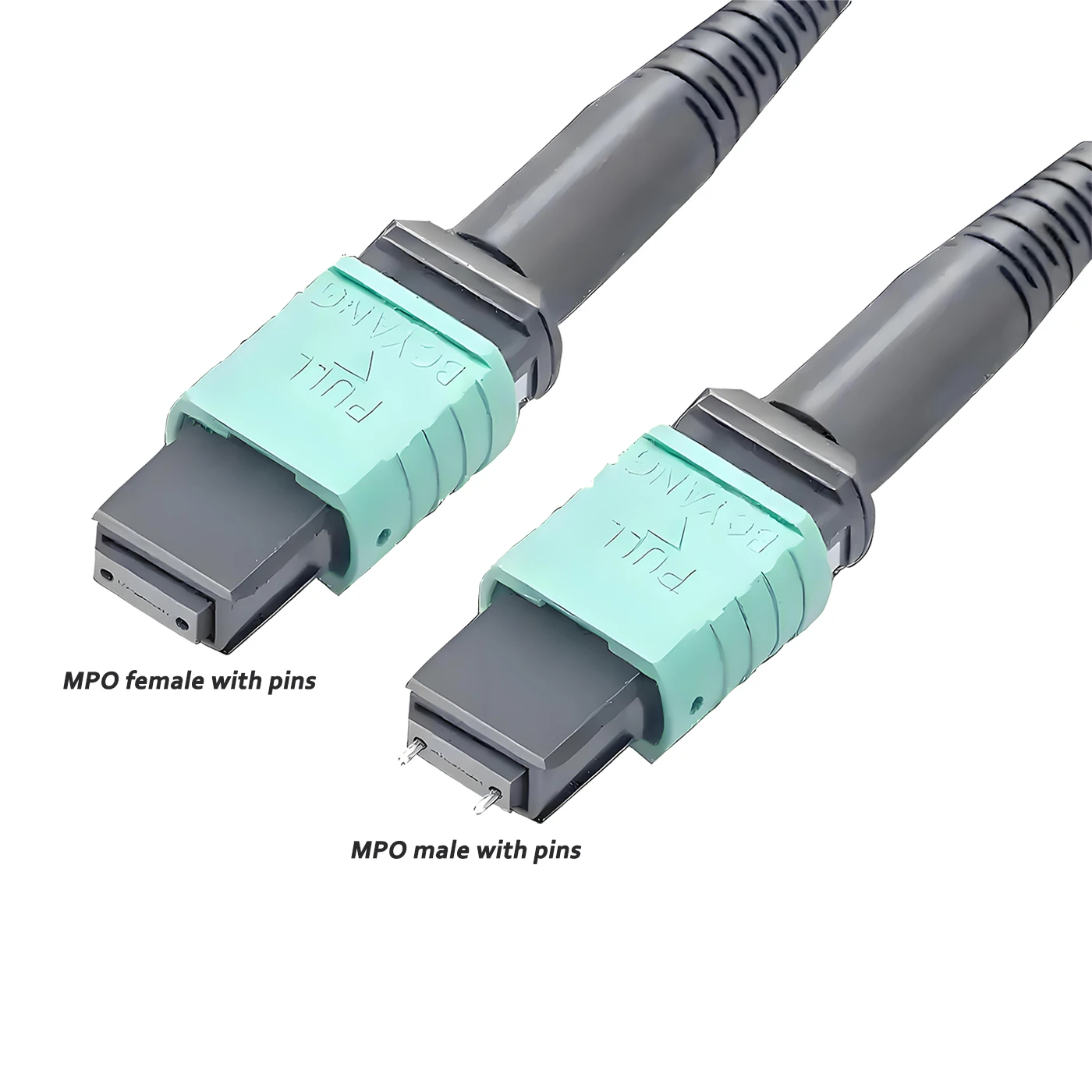
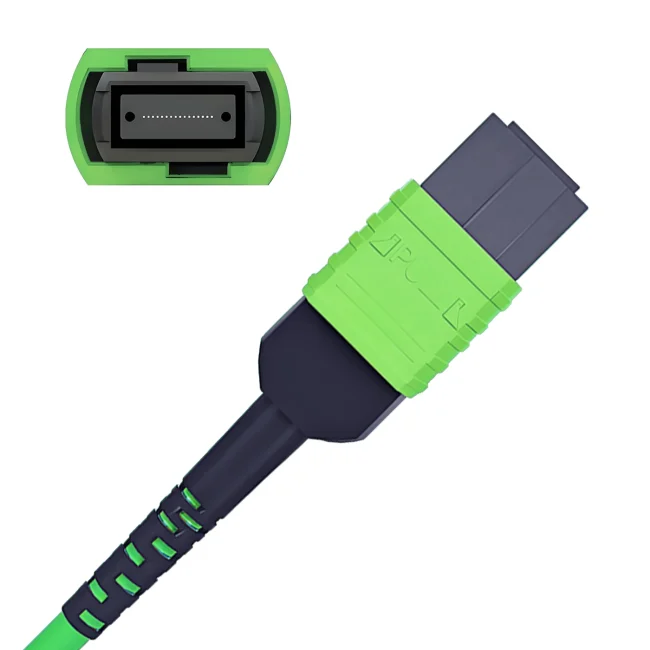
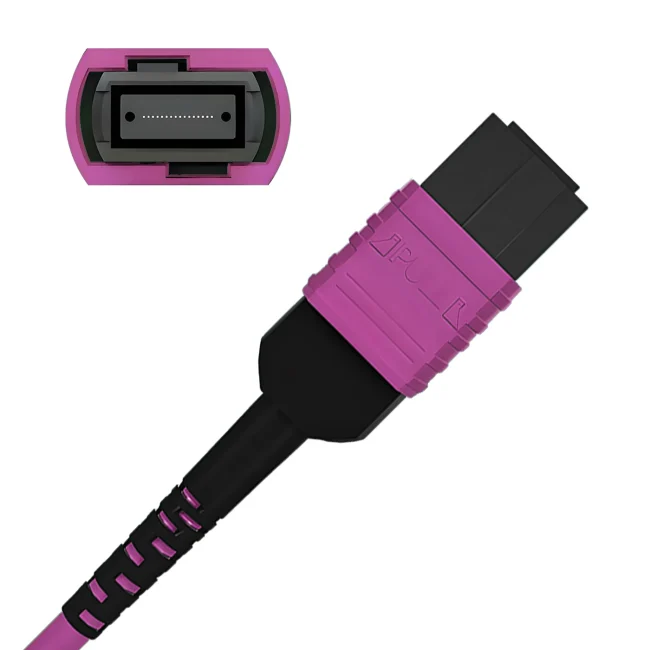
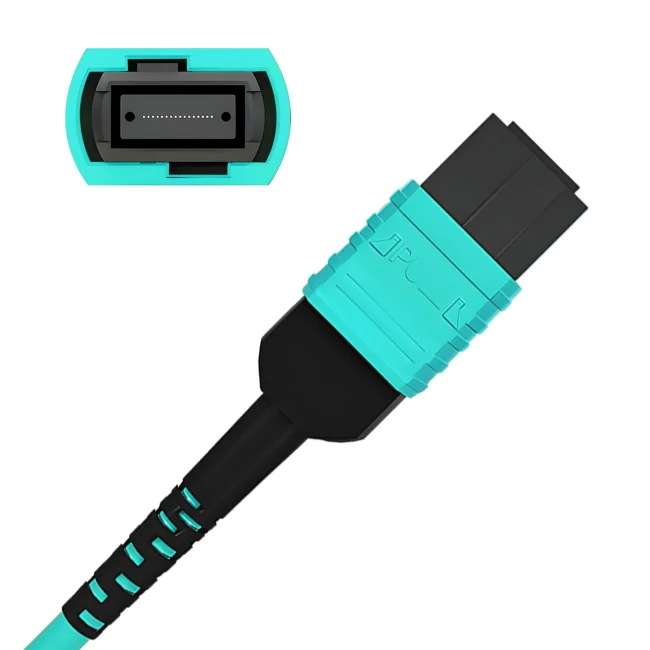
Connector A:US Conec MTP® Elite Female (Pinless)
Connector B:US Conec MTP® Elite Female (Pinless)
Polish Type:UPC to UPC
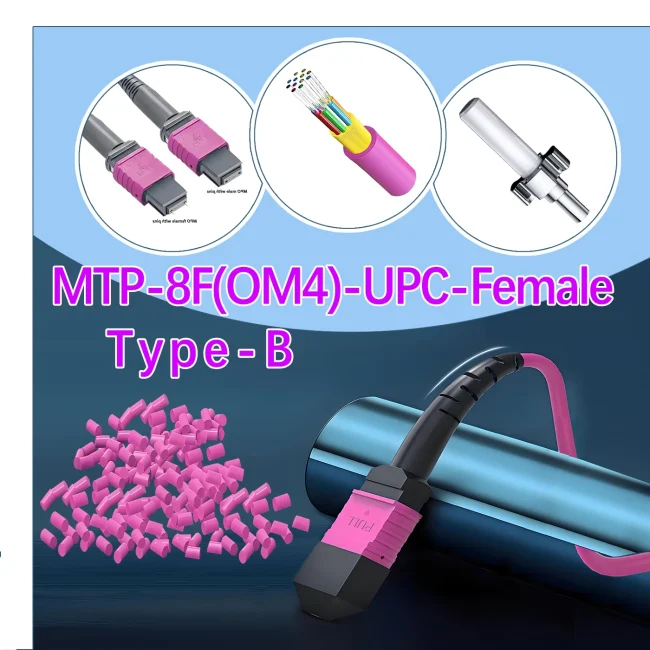
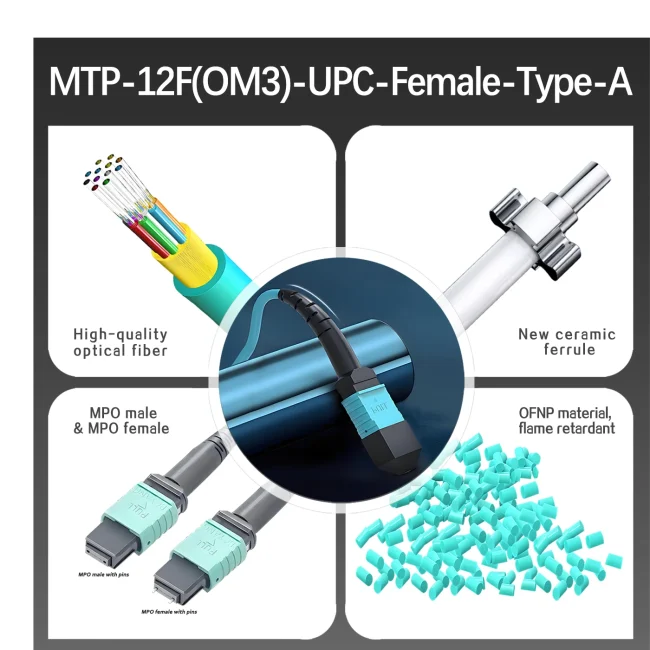
Fiber Mode:OM3 50/125μm
Wavelength:850/1300nm
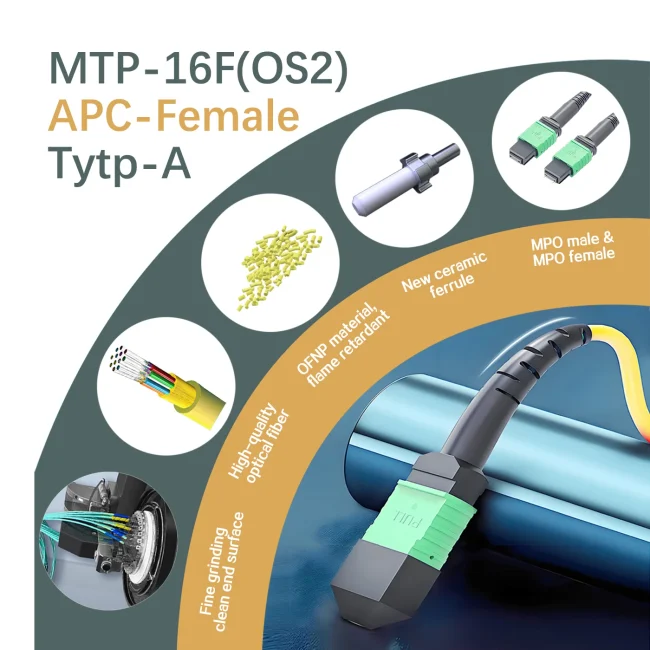
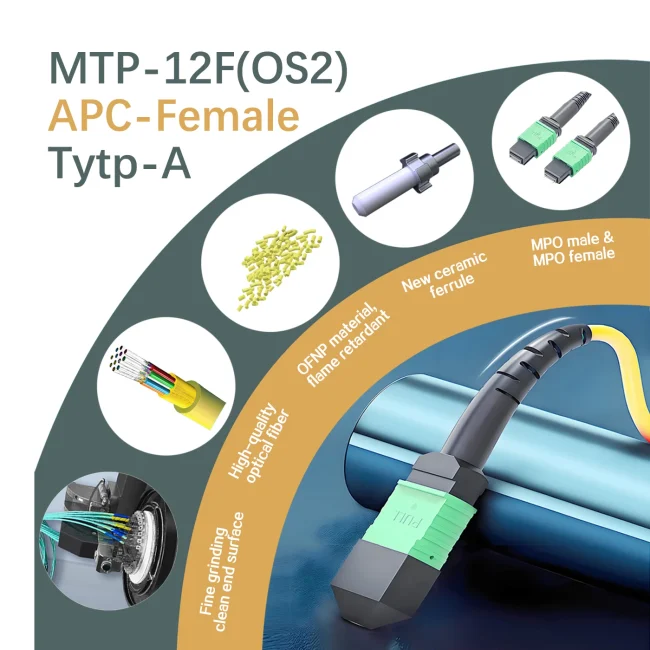
Fiber Count:12 Fibers
Polarity:Type B
Cable Outside Diameter (OD):3.0mm
Cable Jacket:Plenum (OFNP)
Min. Bend Radius (Optical Fiber):7.5mm
Min. Bend Radius (Fiber Cable):20/10D (Dynamic/Static)
Connector Durability:500 times
Tensile Strength:90/180N (Long/Short Term)
Insertion Loss:0.35dB Max
Return Loss:≥20dB
Attenuation at 850nm:≤3.5dB/km
Attenuation at 1300nm:≤1.5dB/km
Operating Temperature:-10 to 60°C (14 to 140℉)
Storage Temperature:-10 to 70°C (14 to 158℉)
*MTP is a registered trademark of US Conec Ltd.
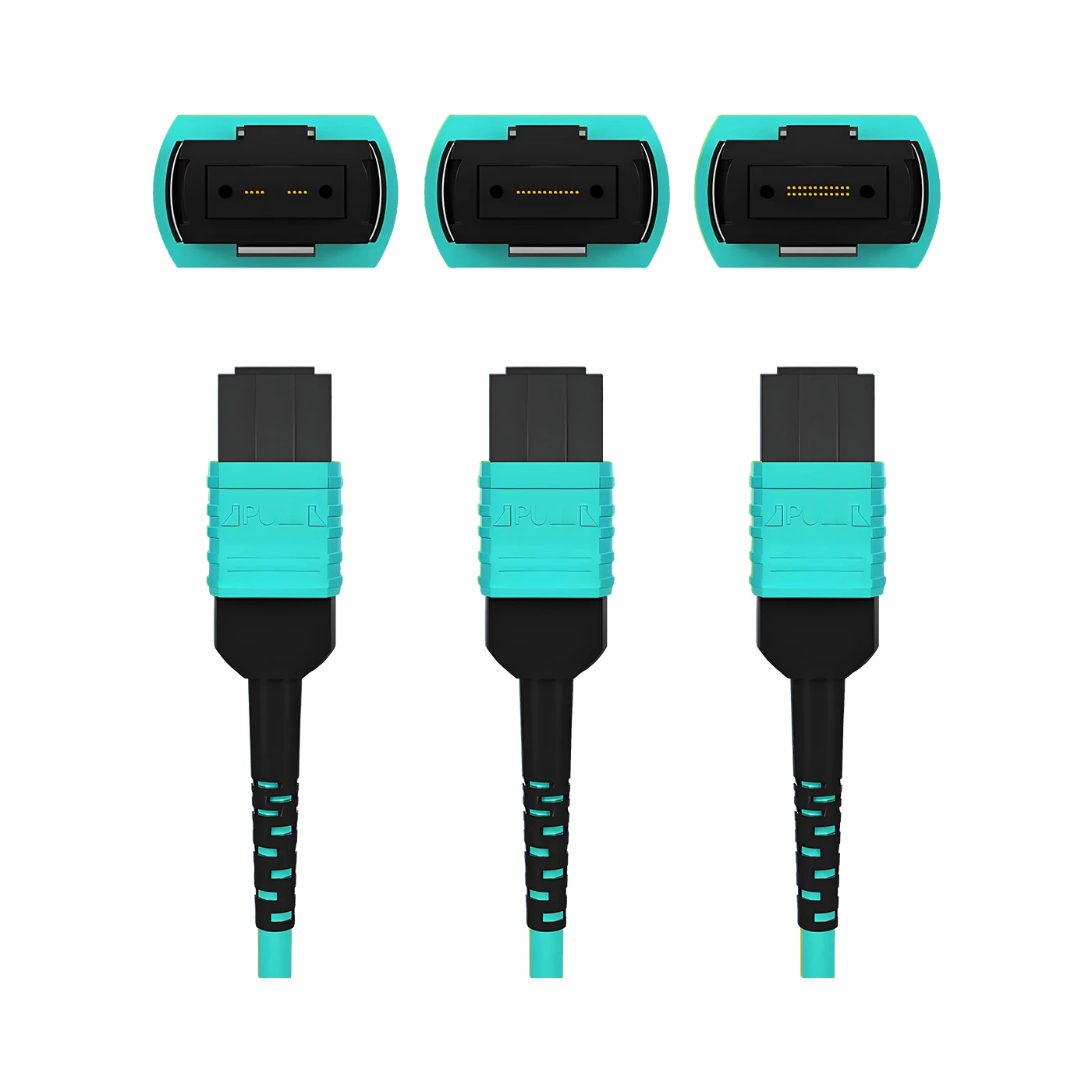
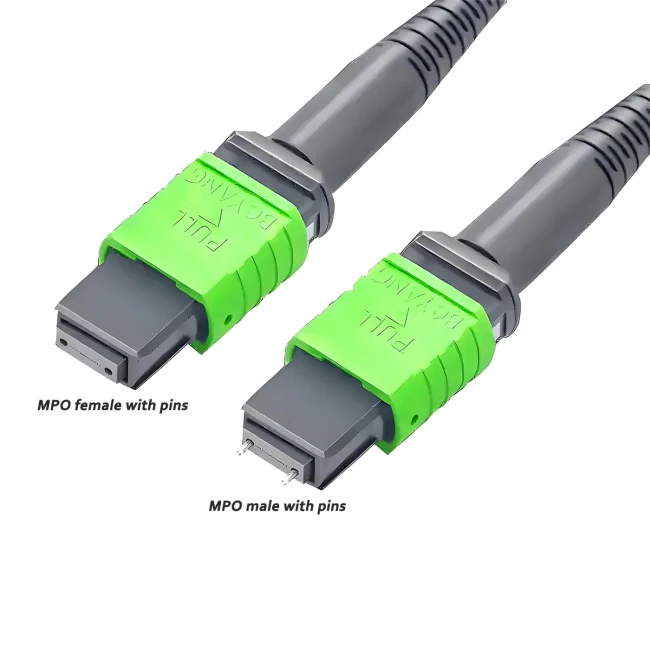
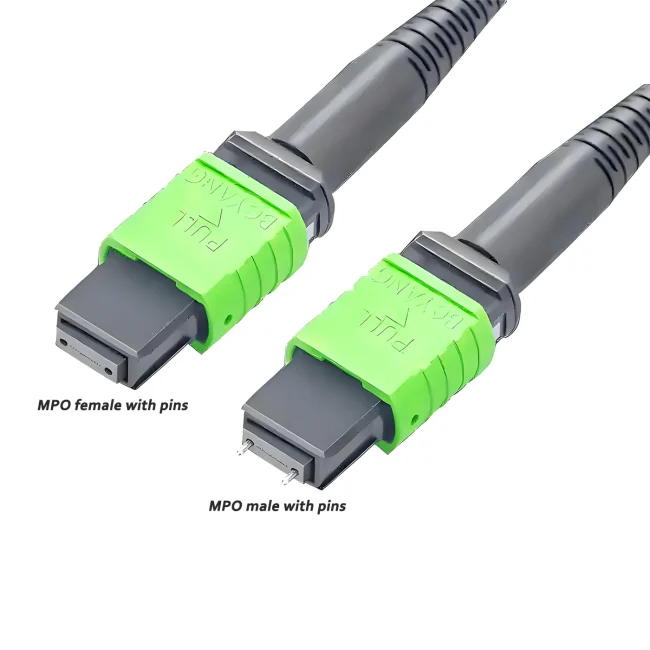
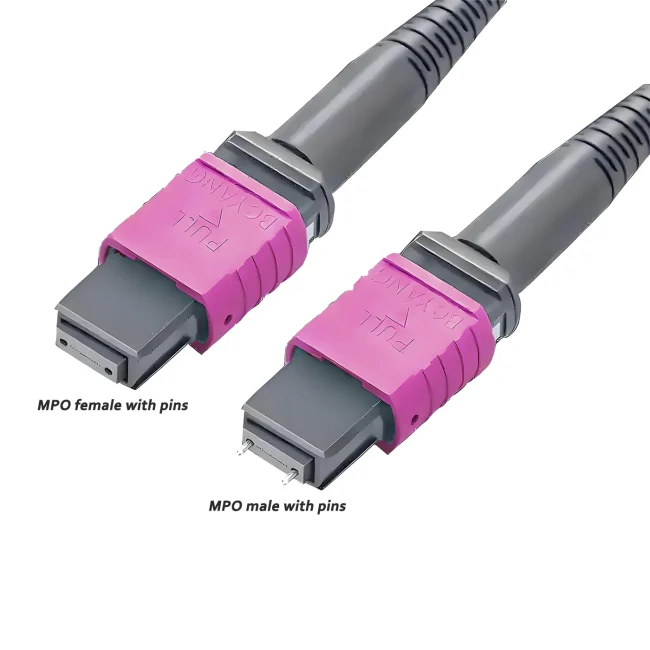
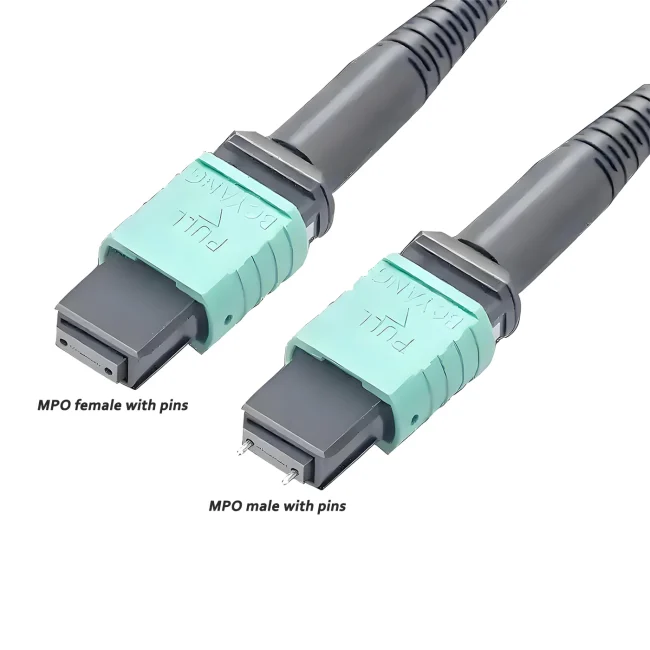
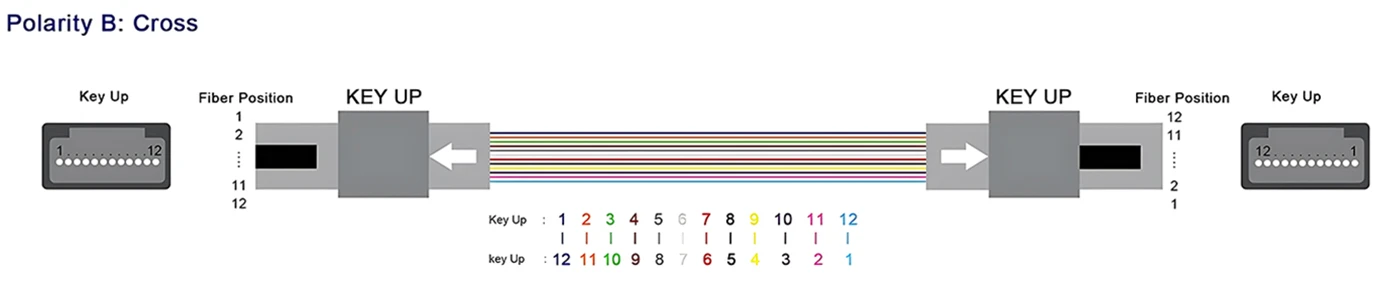
MTP Patch Cable Polarity
The mtp 12 jumper Type B is a high-density multi-fiber connector designed to support fast, efficient connections in modern data centers and high-speed fiber networks. It uses 12 fibers arranged in a single row and follows a specific polarity method to ensure proper signal transmission.
mtp 12 jumper Key Features:
Connector Type:MTP® (a high-performance MPO variant)
Fiber Count:12 fibers in one row
Polarity Type:Type B / cross (reversed or flipped)
Application:40G/100G Ethernet, backbone cabling, parallel optics
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Advantage
- 100% use low-loss connectors
- Each MPO patch cord is fully tested for insertion loss & return loss, 100% tested, and batch goods are not sloppy
- Each line guarantees 3D geometric dimensions and end face integrity, imported equipment measures 3D, and dust-free workshops ensure cleanliness
- Affordable price, quality assurance, source manufacturers take both quality and price into consideration
- All materials have passed REACH/ROHS environmental protection requirements and are of export quality
- Adequate inventory, complete materials, and efficient production
- Customization of special specification MPO patch cords, fast delivery
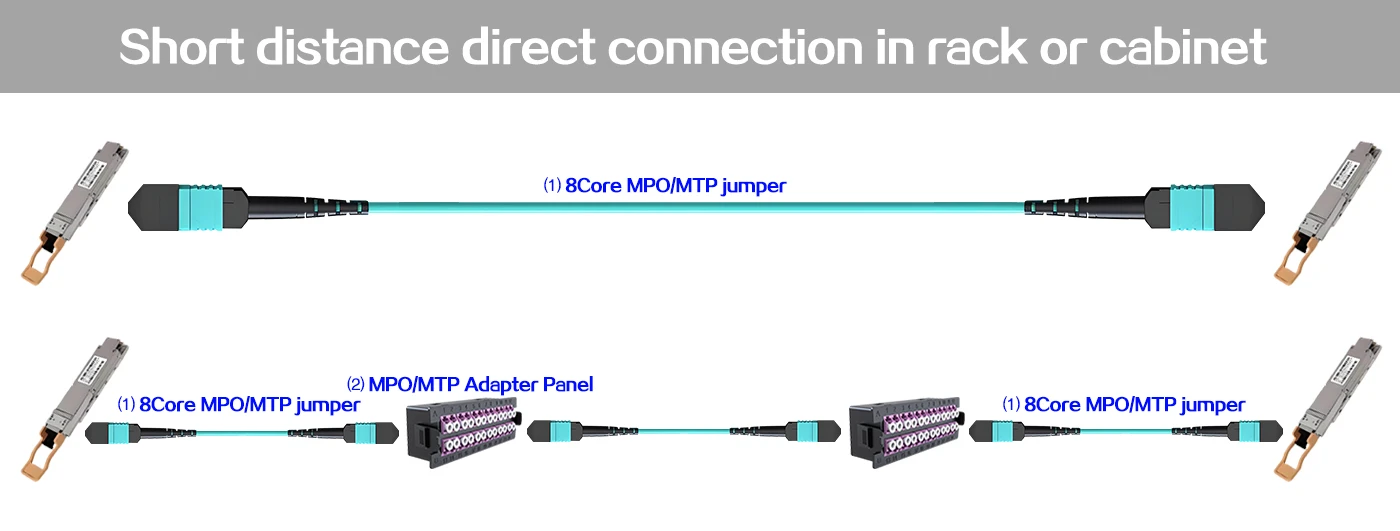
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Short distance direct connection in rack or cabinet
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Duplex fiber interconnection
MTP Fiber Patch Cable 25G-100G direct connection
You can connect one 100G QSFP28 SR4 optical module to four 25G SFP28 SR optical modules through an 8-core MPO/MTP to four duplex LC multimode breakout cable. Similarly, you can connect one 100G QSFP28 PSM4 optical module to four 25G SFP28 LR optical modules through an 8-core MPO/MTP to four duplex LC multimode breakout cable.
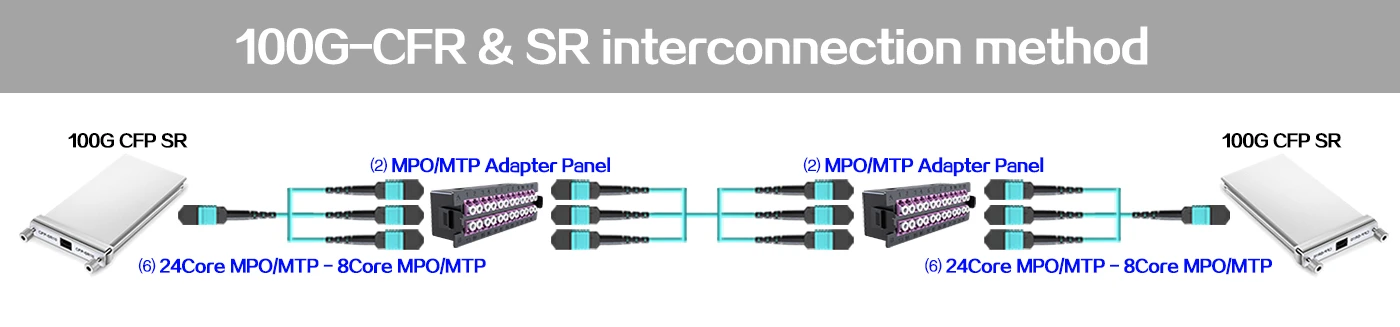
MTP Fiber Patch Cable 100G-CFR&SR interconnection method
The solution is to connect from one 100G CFP optical module to another CFP using a 24-core MPO/MTP to 3×8-core MPO/MTP breakout cable.
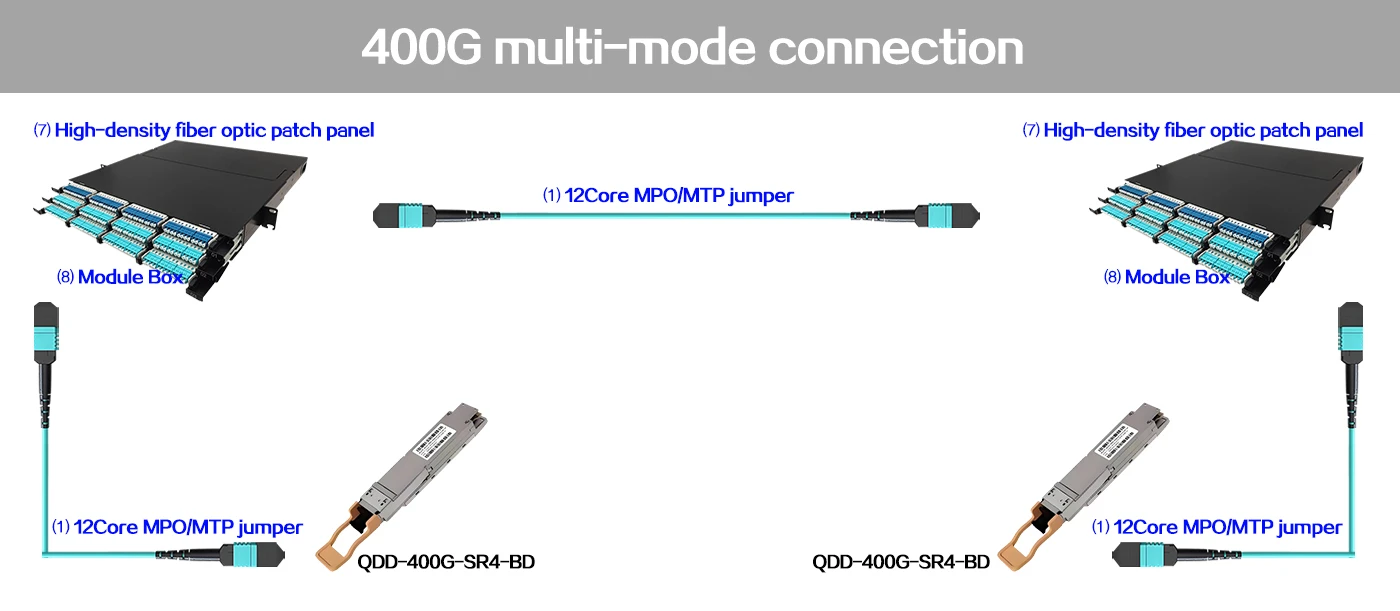
MTP Fiber Patch Cable 400G multi-mode connection
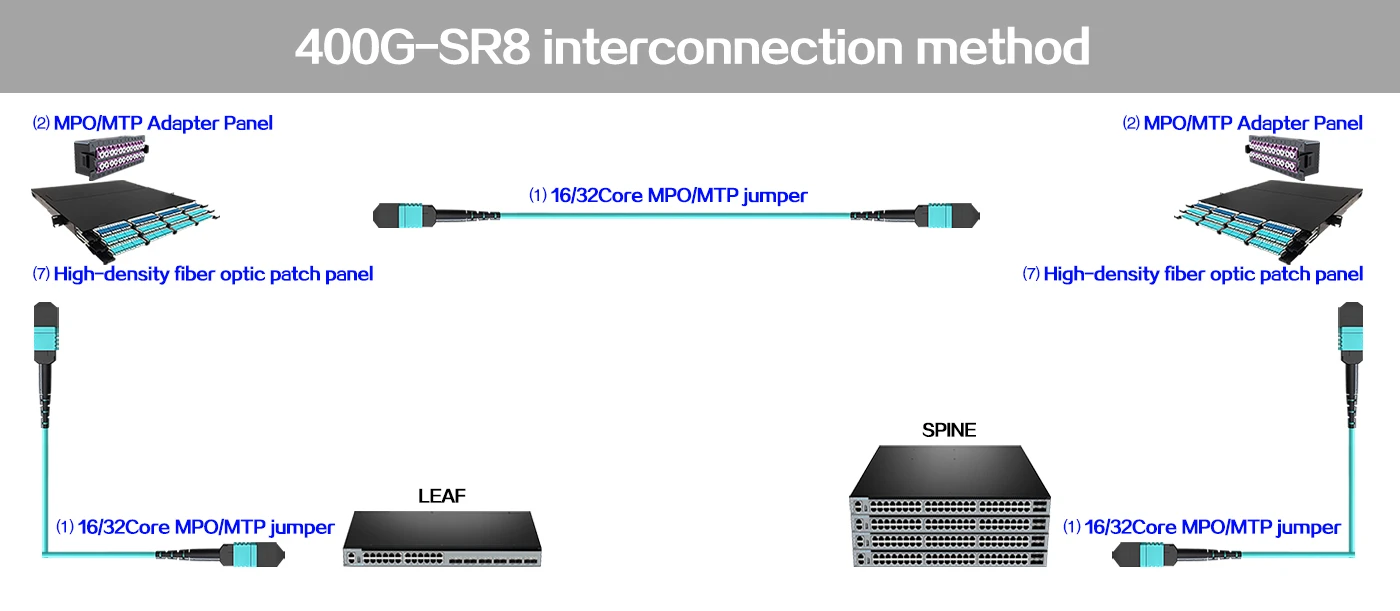
MTP Fiber Patch Cable 400G-SR8 interconnection method
The 400G QSFP-DD SR8 optical module uses a standard MPO-16 connector to achieve 400G transmission. The transmission distance through multimode optical fiber can reach up to 70m (OM3) or 100m (OM4).
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Application
High-speed interconnection in data centers
It is used for direct connection of 40G/100G optical modules, supports 400G high-speed transmission, and can improve wiring density and transmission efficiency. For example, 400G QSFP-DD DR4 optical modules can be directly connected through MPO/MTP-8 multimode fiber jumpers.
High-density wiring scenarios
In the backbone wiring of data centers, MTP/MPO trunk fiber jumpers are used in conjunction with adapter modules to achieve interconnection and cross-connection between devices, saving 45% of wiring space. Branch jumpers are used to connect devices with different rates (such as 10G and 40/100G devices).
100G/400G transmission expansion
Supports branch connection of 100G QSFP28 optical modules to 4 25G SFP28 optical modules, or interconnection of 100G CFP optical modules to another CFP.
Fiber-to-Building Applications
It is used for fiber-to-the-building (FTTB) wiring to meet the needs of high-density fiber access.
MTP Fiber Patch Cable Test Series
MTP Polarity Test Process
End face cleaning: Use special equipment to remove end face contaminants to avoid affecting the test accuracy.
Morphology detection: Analyze the end face microstructure through 3D imaging technology to detect surface roughness, scratches and other defects.
Insertion loss test: Measure the contact loss between the fiber end face and the connector ferrule to evaluate the signal transmission quality.
Polarity verification: Confirm the correspondence between the number of fiber cores and the connector guide hole to prevent communication failure caused by wrong connection.
MTP Test Key Indicators
Cleaning efficiency: It must reach more than 98% to ensure that there are no residual stains on the end face.
Detection accuracy: The resolution of 3D morphology detection must be less than 1.5μ, and the insertion loss error must be controlled within 0.3dB.
Test time: It takes about 10 seconds to detect a single fiber core of a 12-core MPO jumper, and the overall test takes about 2 minutes.
MTP jumper cable Test Common Problems
Pollution sensitivity: Tiny particles on the end face will cause increased loss, and non-contact cleaning methods are required to protect the end face.




























 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart. 
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.